Understanding Structural Steel Fabrication
What is Structural Steel Fabrication?
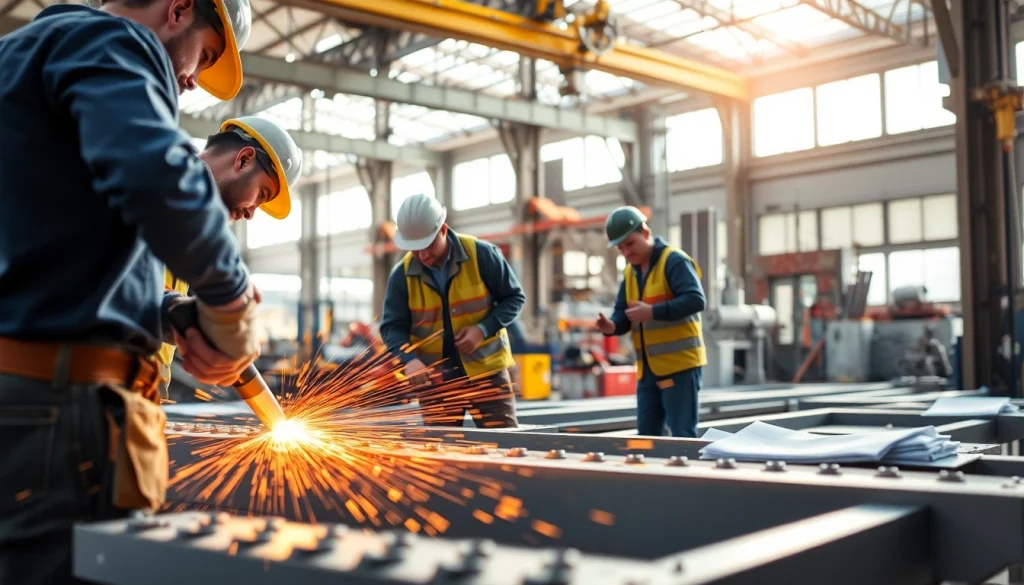
Structural steel fabrication is the intricate process of converting raw steel into finished structural components used in construction projects. This transformative process encompasses everything from cutting and shaping to welding and assembling steel beams, columns, and plates, which are crucial for the structural integrity of buildings and infrastructures. Structural steel fabricators use a variety of techniques and tools to meet the exact specifications required by architects and engineers for their projects. By leveraging advanced technologies, these fabricators turn steel into safe and reliable structural elements that form the backbone of our cities and industries. For those interested in exploring this vital aspect of construction, there is a robust resource dedicated to structural steel fabrication, highlighting its importance and applications.
The Importance of Structural Steel in Construction
Structural steel is a preferred material in the construction industry due to its strength, durability, and versatility. It is crucial for the stability and longevity of buildings, bridges, and various infrastructure projects. The high tensile strength of steel means that it can support significant loads, making it ideal for both tall skyscrapers and expansive industrial facilities. Moreover, structural steel can be prefabricated into various shapes and sizes, allowing for quicker assembly on-site and minimizing construction time. As urban areas continue to evolve, the demand for reliable and sustainable materials like structural steel remains high, enabling engineers and architects to push the boundaries of design.
Basic Processes Involved in Fabrication
The structural steel fabrication process can be broken down into several key stages:
- Cutting: Large steel sections are cut to size using methods like flame cutting, plasma cutting, laser cutting, or water jet cutting.
- Bending: Steel is formed into curves or angles through mechanical bending or rolling processes.
- Welding: Permanent connections between steel sections are made using various welding techniques, including MIG, TIG, and stick welding.
- Assembling: The fabricated parts are assembled into larger structures or components in the fabrication shop.
- Surface Treatment: To ensure longevity and prevent corrosion, the steel may undergo processes like sandblasting and painting.
Techniques and Equipment for Effective Steel Fabrication
Common Tools Used in Structural Steel Fabrication
Effective structural steel fabrication depends significantly on the tools and equipment at the fabricator’s disposal. Some common tools include:
- Shears: Used for cutting sheets of metal into desired sizes.
- Press Brakes: Machines that bend steel sheets or plates to form right angles or other shapes.
- Welding Machines: Essential for joining metal parts permanently.
- Angle Grinders: Tools used for grinding, cutting, and polishing metal surfaces.
- Plasma Cutters: Allow for precise cutting of metal with a plasma torch.
Advanced Fabrication Techniques
As technology advances, so do the techniques used in structural steel fabrication. Some of these advanced techniques include:
- 3D Modeling: Utilized for designing structures before fabrication, allowing for better visualization and error detection.
- Robotic Welding: Automation of the welding process increases efficiency, repeatability, and safety.
- Laser Cutting: Provides precise cuts with minimal material waste, ideal for complex designs.
- Computer Numerical Control (CNC) Machining: Enhances precision in cutting, drilling, and shaping steel components.
Ensuring Precision and Quality Control
Precision is crucial in structural steel fabrication, as even minor deviations can lead to structural failures. Quality control measures must be in place throughout the fabrication process, including:
- Regular Inspections: Employing quality inspectors to ensure adherence to engineering specifications.
- Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs): Establishing detailed processes for each stage of production to maintain consistency.
- Documenting Processes: Keeping detailed records of each fabrication project to facilitate evaluation and improvement.
Best Practices for Structural Steel Fabrication Projects
Planning and Design Considerations
A successful structural steel fabrication project begins with thorough planning and design. Key considerations include:
- Design for Manufacturability: Designing components that are easy to fabricate and assemble will streamline production.
- Material Selection: Choosing the right grade of steel based on the project’s load requirements and environmental conditions.
- Collaboration with Engineers: Engaging with structural engineers early in the planning phase can help anticipate challenges.
Cost Management in Steel Fabrication
Effective cost management is essential to ensure a project remains profitable. Factors influencing costs include:
- Material Costs: Fluctuations in steel prices can impact overall project budgets.
- Labor Costs: Skilled labor is essential for quality fabrication; thus, labor rates should be carefully managed.
- Overhead Costs: Maintaining equipment and managing shop facilities add to the overall budget and should be accounted for in project estimates.
Safety Standards and Protocols
Implementing robust safety standards and protocols is vital to protect workers during the fabrication process. Important practices include:
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Ensuring all workers are equipped with safety gear such as helmets, gloves, and eye protection.
- Safety Training: Regular training programs to familiarize workers with safety protocols and emergency response procedures.
- Hazard Assessments: Conducting frequent evaluations of work areas to identify and mitigate safety risks.
Current Trends in the Structural Steel Fabrication Industry
Market Growth and Future Projections
The structural steel fabrication market has shown remarkable growth, projected to expand from approximately USD 87.5 billion in 2024 to over USD 120 billion by 2031. This growth will largely be driven by increasing urbanization, infrastructure development, and rising construction activities globally. Industry experts foresee significant opportunities for companies that adapt to changing technologies and market demands.
Technological Advancements Impacting Fabrication
Technological advancements are reshaping the structural steel fabrication landscape. Innovations such as Building Information Modeling (BIM) allow for collaborative design processes, enhancing efficiency from the initial design phase through to construction. Additionally, the rise of digital fabrication methods enables rapid prototyping and the ability to create complex geometries that were previously unfeasible.
Sustainability Practices in Steel Manufacturing
With an increased emphasis on sustainability, the structural steel fabrication industry is incorporating eco-friendly practices. These include:
- Recycling Steel: Steel is one of the most recycled materials globally, minimizing waste and reducing the need for new raw materials.
- Energy Efficiency: Implementing energy-efficient manufacturing processes to reduce the carbon footprint associated with steel production.
- Green Building Certifications: Aiming for certifications that recognize sustainable building practices can enhance the marketability of projects.
Case Studies and Real-World Applications
Successful Structural Steel Fabrication Projects
Numerous successful projects highlight the capabilities of modern structural steel fabrication. For instance, projects like the Burj Khalifa in Dubai and the One World Trade Center in New York showcase how advanced fabrication techniques contribute to creating iconic structures that push the limits of engineering and architectural design.
Lessons Learned from Industry Leaders
Industry leaders emphasize several lessons from their experiences in structural steel fabrication, such as:
- Embrace Innovation: Continuous adoption of the latest technologies is essential for staying competitive.
- Focus on Team Training: Investing in the training of personnel ensures higher quality work and safety on the job.
- Build Strong Relationships: Collaborating with suppliers and stakeholders leads to better project outcomes.
Innovations Shaping the Future of Fabrication
The future of structural steel fabrication will be influenced by emerging trends like smart fabrication plants, where the use of IoT devices enables real-time monitoring of processes, improving efficiency and reducing downtime. Furthermore, advancements in AI and machine learning are set to enhance decision-making in design and manufacturing processes, propelling the industry into a new era of innovation.