Understanding Structural Steel Fabrication
Definition and Importance of Structural Steel Fabrication
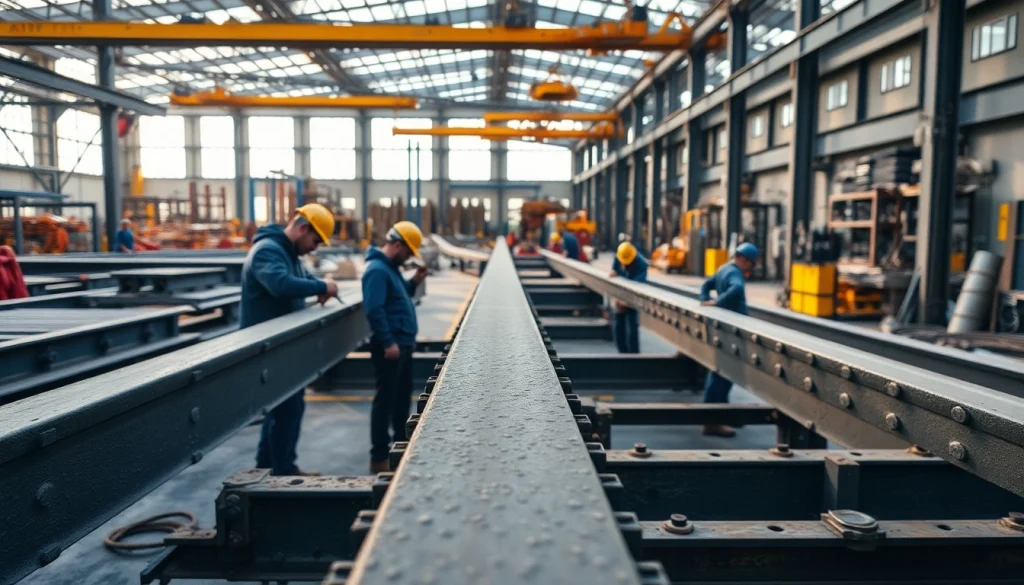
Structural steel fabrication is a crucial process in the construction industry. It involves the cutting, shaping, and assembling of steel to create components that form the framework for buildings and other structures. This process is integral to ensuring that the structures are safe, durable, and capable of withstanding various loads and forces. The importance of structural steel fabrication cannot be overstated; it not only helps in creating reliable foundations but also enables architects and engineers to design innovative structures with increased aesthetic appeal and functionality.
Within the realm of structural steel fabrication, several techniques are used to achieve precise specifications and high-quality outcomes, thus enhancing the overall strength, longevity, and performance of the structures being built.
Common Applications and Industries
Structural steel fabrication serves a diverse range of industries. Key applications include:
- Commercial Buildings: Offices, shopping malls, and other commercial spaces rely on steel frameworks for support.
- Residential Construction: Single-family homes and multi-family dwellings benefit from steel’s strength, enabling complex designs that use open floor plans.
- Infrastructure Projects: Bridges, highways, and railways require robust steel structures to endure significant stresses and traffic loads.
- Industrial Facilities: Factories and warehouses often need large, open spaces that are efficiently created using structural steel.
- Energy Sector: Wind farms and power plants often utilize steel fabrication in their construction processes to ensure stability and reliability.
Key Materials Used in Fabrication
Understanding the materials used in structural steel fabrication is essential to grasp its importance in construction. The primary material is, as one might expect, steel. Various grades of steel, such as carbon steel, alloy steel, and stainless steel, are commonly utilized:
- Carbon Steel: Often used for structural purposes due to its good tensile strength and ductility.
- Alloy Steel: Contains elements like chromium and nickel, enhancing specific properties like corrosion resistance and strength at elevated temperatures.
- Stainless Steel: Known for its corrosion resistance properties, it is often used in applications exposed to harsh environments.
Processes Involved in Structural Steel Fabrication
Cutting Techniques and Technology
The cutting process is pivotal in structural steel fabrication and significantly impacts the overall outcome. Various cutting techniques are employed, including:
- Shearing: A method that utilizes scissors-like mechanics to cut metal sheets and plates.
- Flame Cutting: Uses a high-temperature flame to melt and cut through thick steel materials.
- Plasma Cutting: Employs plasma torches that produce high-temperature ionized gas to cut through various thicknesses of steel efficiently.
- Water Jet Cutting: Utilizes high-pressure water mixed with abrasives to cut materials, offering precision without affecting the material’s properties.
The choice of cutting method depends on factors such as the thickness of the material, design specifics, and cost considerations.
Welding Methods and Standards
Welding is a critical component in the assembly of fabricated steel structures. Several welding methods are commonly used:
- MIG Welding (Metal Inert Gas): A versatile method that provides strong welds suitable for various applications.
- TIG Welding (Tungsten Inert Gas): Offers high precision and is ideal for intricate designs.
- Stick Welding (Shielded Metal Arc Welding): A traditional method that remains essential for outdoor applications due to its ability to produce strong welds in various positions.
Adherence to welding standards, such as those established by the American Welding Society (AWS), is vital to ensure the integrity and safety of welded joints within structural steel products.
Finishing and Coating Options
Finishing processes play a vital role in enhancing the durability and aesthetics of structural steel. Common finishing techniques include:
- Powder Coating: A process that applies a protective layer, offering resistance to corrosion and wear.
- Galvanizing: A technique that involves coating steel with zinc to protect it from corrosion.
- Painting: An essential practice to add aesthetic appeal while protecting structural elements from environmental damage.
Choosing the correct finishing technique is essential based on environmental conditions and expected lifespan of the structure.
Quality Control in Structural Steel Fabrication
Testing Methods for Structural Integrity
Quality control is paramount in structural steel fabrication to ensure that products meet relevant safety and performance standards. Common testing methods include:
- Ultrasonic Testing: Utilizes high-frequency sound waves to detect internal flaws within steel material.
- Magnetic Particle Testing: Identifies surface and near-surface defects by applying magnetic fields and particles.
- Radiographic Testing: Uses X-rays or gamma rays to examine the internal structure of materials, ensuring integrity.
Implementing robust testing protocols helps to identify potential weaknesses early on, preventing costly repairs and ensuring safety.
Compliance with Industry Standards
Fulfilling industry standards and regulations is essential for structural steel fabrication processes. Standards set by organizations such as the American Institute of Steel Construction (AISC) and OSHA ensure that both materials and practices are safe and reliable. Compliance not only guarantees quality but also fosters trust with clients and stakeholders.
Ensuring Safety in Fabrication Practices
Safety is a non-negotiable aspect of structural steel fabrication. Implementing rigorous safety protocols, including regular safety training, using personal protective equipment (PPE), and maintaining clean, organized workspaces, minimizes risks. Additionally, conducting regular safety audits helps identify and mitigate potential hazards.
Advantages of Professional Structural Steel Fabrication
Cost-Effectiveness and Efficiency
Choosing professional structural steel fabrication services leads to significant cost savings and efficiency. Skilled fabricators utilize advanced technology and streamlined processes to minimize waste and optimize materials, ultimately reducing labor costs and project timelines.
Customization and Design Flexibility
Professional fabrication offers unmatched customization options that cater to diverse architectural designs. By leveraging advanced fabrication technology, clients can achieve unique designs that standard materials simply cannot provide. This flexibility allows for the integration of specific functionalities and aesthetics into any project.
Impact on Project Timelines
Efficient structural steel fabrication accelerates project timelines. By collaborating with seasoned professionals, construction teams can ensure timely delivery of fabricated components, allowing projects to progress smoothly. This predictability is paramount in maintaining schedules and managing project budgets effectively.
Future Trends in Structural Steel Fabrication
Sustainability in Steel Fabrication
The future of structural steel fabrication is increasingly revolving around sustainability. The industry is witnessing a shift toward using recycled materials and adopting greener fabrication practices. Incorporating energy-efficient processes not only reduces costs but is also a critical factor in promoting an eco-friendly construction environment.
Technological Advancements and Automation
Automation and advanced technological solutions are transforming the structural steel fabrication landscape. From robotic welding to AI-driven quality control, technology is enhancing efficiency, precision, and safety. Embracing these innovations will allow fabricators to remain competitive and respond to the growing market demands more effectively.
Global Market Trends and Insights
The global structural steel fabrication market is projected to grow substantially over the next few years, driven by urbanization and infrastructure development. Emerging markets are expected to witness significant demand, and companies that adapt to changing regulations and technologies will thrive. Understanding these trends will empower industry players to navigate the challenges and seize opportunities within this dynamic marketplace.